What do you need?The greenhouse effect keeps the temperatures on our planet mild and suitable for living things Greenhouse gases (GHG) include carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, ozone, nitrous oxide and fluorinated gases These molecules in our atmosphere are called greenhouse gasesMethane is the next of the greenhouse gases which has the biggest effect on global warming (15%) This is generated by activities such as livestock production, agriculture, sewage treatment, natural gas and oil distribution , coal mining, fuel use and is also given off from waste tips It lasts an average of 12 years in the atmosphere

The Discovery Of Global Warming International Brotherhood Of Boilermakers
Greenhouse gas effect definition
Greenhouse gas effect definition-Human Activity and the Greenhouse Effect What greenhouse gases do humans generate?Too much greenhouse effect The atmosphere of Venus, like Mars, is nearly all carbon dioxide But Venus has about 154,000 times as much carbon dioxide in its atmosphere as Earth (and about 19,000 times as much as Mars does), producing a runaway greenhouse effect and a surface temperature hot enough to melt lead




Climate Change And Greenhouse Gas Emissions City Of Lakewood
Greenhouse gases have very different warming effects one tonne of methane does not have the same impact on warming as one tonne of CO 2 Carbon dioxide equivalents (CO 2 e) attempt to convert the warming impact of the range of greenhouse gases into a single metricThe Greenhouse Effect Goal Students will learn how greenhouse gases temporarily trap heat within Earth's atmosphere, warming our planet via the greenhouse effect Activity Students explore the greenhouse effect through computer simulations and then dive deeper learning how the greenhouse effect works via readings and videos onlineWater vapor is known to be Earth's most abundant greenhouse gas, but the extent of its contribution to global warming has been debated Using recent NASA satellite data, researchers have estimated more precisely than ever the heattrapping effect of water in the air, validating the role of the gas as a critical component of climate change
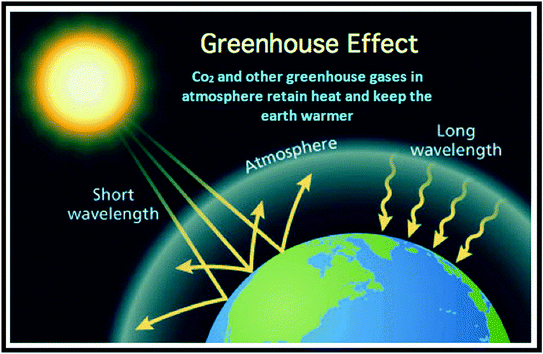
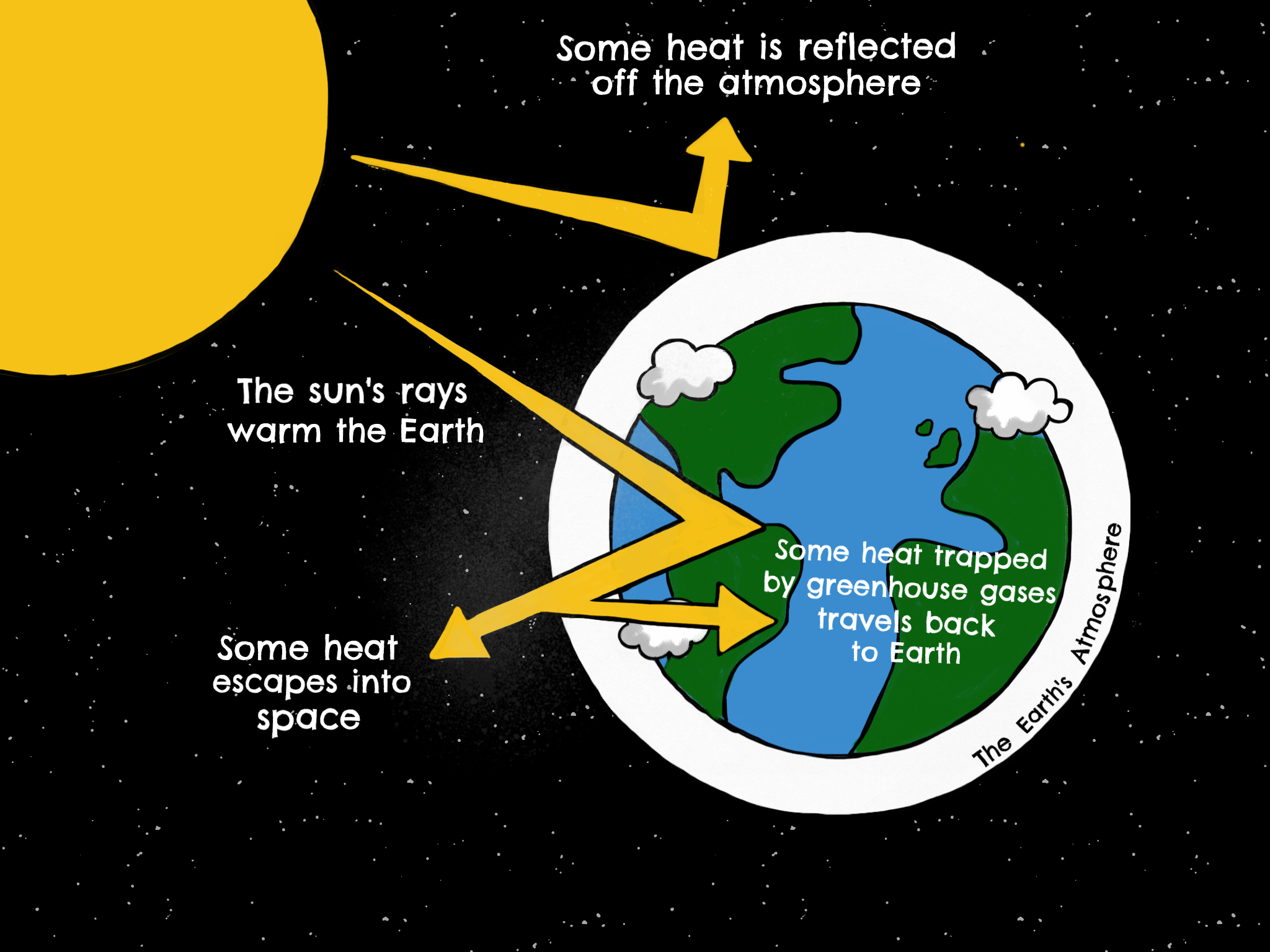
This is called the "greenhouse effect" Up to a point, the greenhouse effect helps keep the Earth at a temperature suitable for life As more greenhouse gases are pumped into the atmosphere, however, the temperature increases and there's a risk of creating feedback effects that could make the Earth warmer stillMuch like the glass of a greenhouse, gases in Earth's atmosphere sustain life by trapping the sun's heat These "greenhouse gases" allow the sun's rays to pass through and warm the planet but prevent this warmth from escaping the atmosphere into space Without them, Earth would be too cold to sustain life as we know it The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases (ie, greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiate
Greenhouse effect The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface When the Sun's energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and reradiated by greenhouse gases Greenhouse gases are gases in Earth's atmosphere that trap heat They let sunlight pass through the atmosphere, but they prevent the heat that the sunlight brings from leaving the atmosphere The main greenhouse gases areConcentration, or abundance, is the amount of a particular gas in the air Larger emissions of greenhouse gases lead to higher concentrations in the atmosphere Greenhouse gas concentrations are measured in parts per million, parts per billion, and even parts per trillion




The Greenhouse Effect And The Global Warming By Rajen Raj Barua Phd Linkedin




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
Tyndall soon established that carbon dioxide and water vapour were among the gases that absorbed heat, and also that they radiated heat, the physical basis of the greenhouse effect In making these discoveries, Tyndall set the foundation for our modern understanding of the greenhouse effect, climate change, meteorology, and weatherThe greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gas es—collect in Earth's atmosphere These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxide, and fluorinate d gases sometimes known as If you made our Gummy Greenhouse Gas models, you may wonder why the molecules you made with gumdrops are called greenhouse gases Here is why If the atmosphere contains too much of these gases, the whole Earth becomes a hotter and hotter greenhouse The atmosphere holds onto too much of the heat at night instead of letting it escape into space




The Discovery Of Global Warming International Brotherhood Of Boilermakers




Greenhouse Effect How Does Climate Change Work
The increased greenhouse effect is causing changes in our planet that can affect our lives The major Greenhouse Gas, carbon dioxide, emitted naturally and by the burning of fossil fuels, stays in the atmosphere a long time Its warming effect occurs even when the sky is clear and dry Climate scientists are so concerned about carbon dioxide Scientists know with virtual certainty that increasing greenhouse gas concentrations tend to warm the planet In computerbased models, rising concentrations of greenhouse gases produce an increase in the average surface temperature of the earth over timeChange the greenhouse gas concentration and see how the temperature changes Then compare to the effect of glass panes Zoom in and see how light interacts with molecules Do all atmospheric gases contribute to the greenhouse effect?




Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Definition Solution Facts




The Greenhouse Effect World101
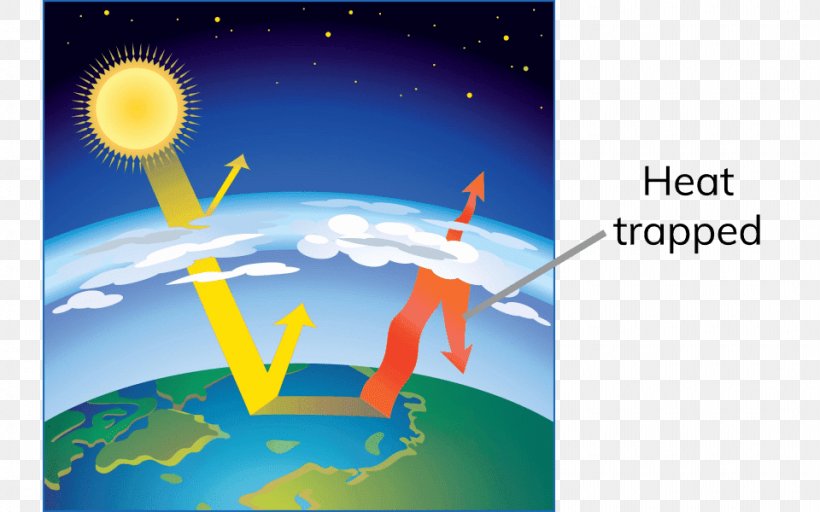
The gases formed by the burning, such as carbon dioxide, are building up in the atmosphere They act like greenhouse glass The result, experts believe, is that the Earth heating up and undergoing global warming How can you show the greenhouse effect?An increase in the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases produces a positive climate forcing, or warming effect From 1990 to 19, the total warming effect from greenhouse gases added by humans to the Earth's atmosphere increased by 45 percent The warming effect associated with carbon dioxide alone increased by 36 percentThe heated layer can then radiate energy back to Earth's surface This effect of trapping the outgoing longwave radiation and warming up Earth's atmosphere and surface is referred to as the Greenhouse effect and the gases that absorb longwave radiation and create the greenhouse effect are called Greenhouse gases (GHGs)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-474143192-5b7df4fdc9e77c0050c92479.jpg)



Greenhouse Gas Effects On The Economy




Textbook Representation Of The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas Layer Download Scientific Diagram
The greenhouse effect Without greenhouse gases in its atmosphere, the Earth would be about 18°C colder on average than it is now That would make it too cold to support life as we know itEvery day we generate greenhouse gases through interaction with factories, agriculture, and cars Our activities produce four major greenhouse gases (Figure 1) Carbon dioxide (CO2) Carbon dioxide enters the atmosphere throughGreenhouse Gases and Temperature A greenhouse gas (GHG) is any gas in the atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation in the thermal infrared range These are the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect, which results in increased temperatures on Earth The greenhouse effect occurs as the gases reach Earth's surface



What Are Greenhouse Gases Environnet




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica
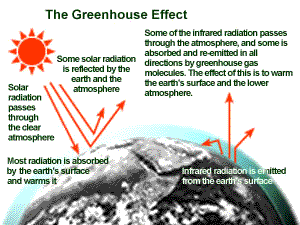
Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth 's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect greenhouse effect on Earth The greenhouse effect on EarthHow the greenhouse effect works It's thought that the buildup of greenhouse gases impacts on global temperature in two ways The gases allow more of the sun's rays to enter the atmosphereGreenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water



Reducing The Impacts Of Greenhouse Gases Springerlink




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
Human emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases – are a primary driver of climate change – and present one of the world's most pressing challenges 1 This link between global temperatures and greenhouse gas concentrations – especially CO 2 – has been true throughout Earth's history 2 To set the scene, let's look at how the planet has warmed Greenhouse gases are gases in the Earth's atmosphere that produce the greenhouse effect Changes in the concentration of certain greenhouse gases, from human activity (such as burning fossil fuels), increase the risk of global climate change Greenhouse gases include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane, nitrous oxide, halogenated "This effect would cause significant warming even if carbon dioxide were not a greenhouse gas" Its a doublewhammy CO2 traps heat requiring plants to do more evaporative cooling, but CO2 acts to decrease a plant's ability to cool itself




27 Greenhouse Gases Ideas Greenhouse Gases Gas Greenhouse



Humans And The Greenhouse Effect Climate Institute
The 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into spaceTwo identical glass jars 4 cups cold water 10 ice cubesHow do greenhouse gases affect the climate?




The Greenhouse Effect Climate Matters



Misconception Monday Is Greenhouse Misleading National Center For Science Education
These gases are known as greenhouse gases Below are the most important greenhouse gases that influence Earth's climate system Water vapor (H2O) is the strongest greenhouse gas, and the concentration of this gas is largely controlled by the temperature of the atmosphere As air becomes warmer, it can hold more moisture or water vapor Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs lived The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphere Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases




1 Greenhouse Gas Effect Society For The Preservation Of Wild Culture Download Scientific Diagram



The Greenhouse Effect
Amplifying the greenhouse effect Like other gases in the atmosphere, including oxygen and nitrogen, greenhouse gases are largely transparent to incoming sunlight Unlike those more abundant gases though, greenhouse gases are not transparent to heat (longwave infrared radiation) The sunwarmed surface of Earth radiates heat day and nightGreenhouse gases reflect infrared radiation, so some of the heat leaving the Earth bounces off the greenhouse gases in our atmosphere and comes back to the Earth's surface This is called the "greenhouse effect," in a comparison to the heattrapping glass on a greenhouse The greenhouse effect is not a bad thingGreenhouse Gas (GHG) Reduction As outlined in Executive Order (EO) , Planning for Federal Sustainability in the Next Decade, the goal of reducing greenhouse gas emissions is to minimize the contributions to the greenhouse effect which contributes to global warming and subsequent adverse environmental and human healthGHG reduction is managed by the following




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate



Earth Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas Atmosphere Png 960x600px Earth Atmosphere Atmosphere Of Earth Brand Climate Download
Explore the atmosphere during the ice age and today What happens when you add clouds? The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides




Explaining The Greenhouse Effect Sustainability Youtube




File Earth S Greenhouse Effect Us Epa 12 Png Wikimedia Commons




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




How Greenhouse Gases Influence Climate The Weather Gamut



The Greenhouse Effect 1



Introduction To Greenhouse Gases Industry And Climate Change
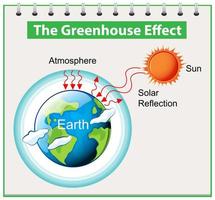



Greenhouse Gas Vector Art Icons And Graphics For Free Download




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Climate Change And Greenhouse Gas Emissions City Of Lakewood




15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases




Global Human Green House Gas Emissions By Sector Greenhouse Gases Ghg Emissions Emissions




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids
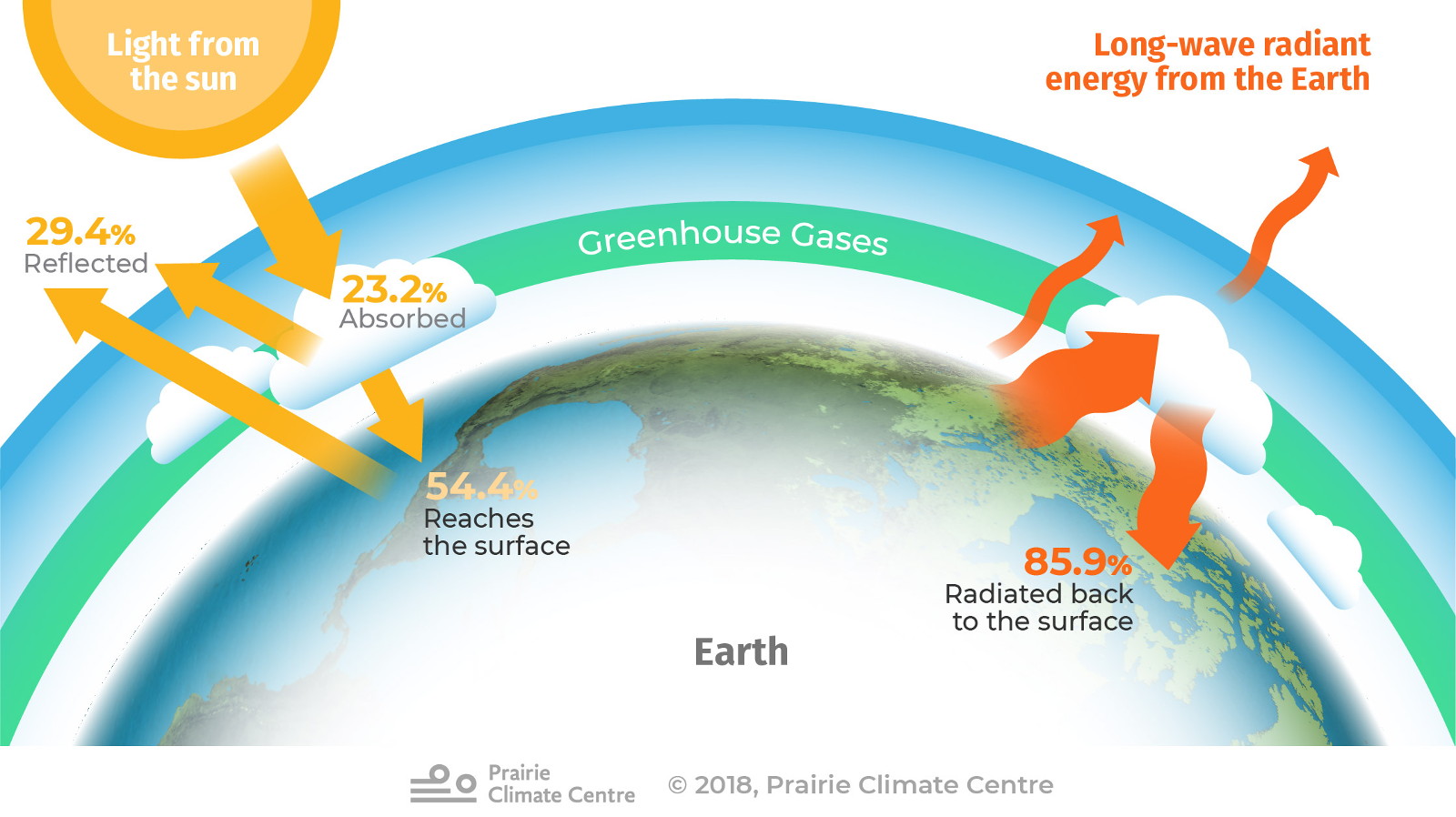



Greenhouse Gases Climate Atlas Of Canada
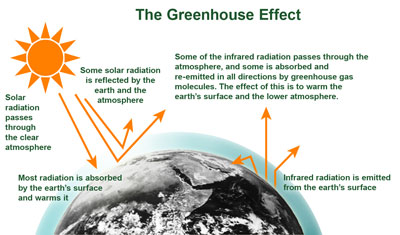



The Effect Of Climate Change On Water Resources And Programs Watershed Academy Web Us Epa



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
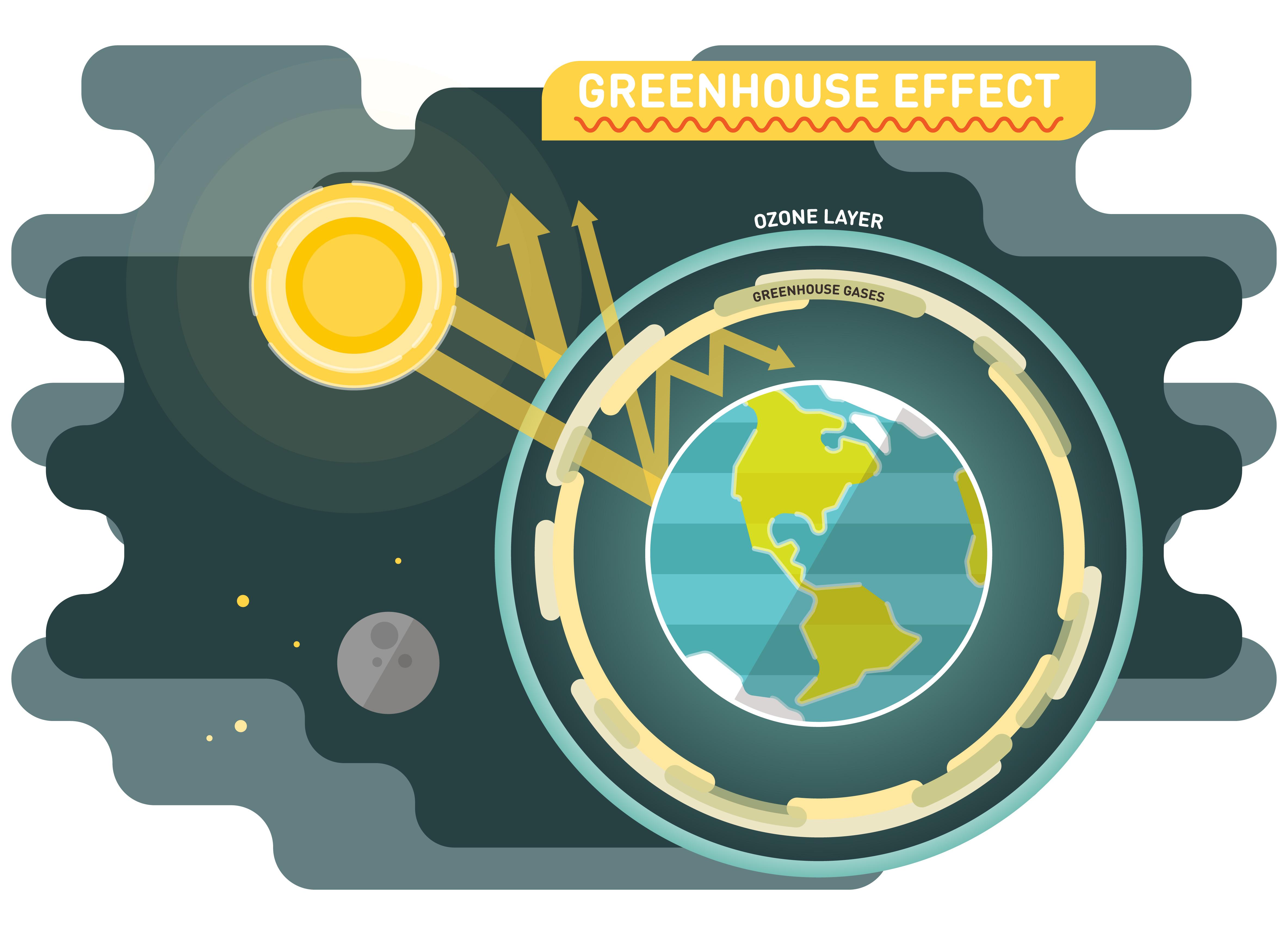



Why The Greenhouse Effect Is Important How It Affects The Climate



Untitled Document




Greenhouse Effect High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




Greenhouse Gas Effect Stock Image C033 5439 Science Photo Library




The Greenhouse Effect
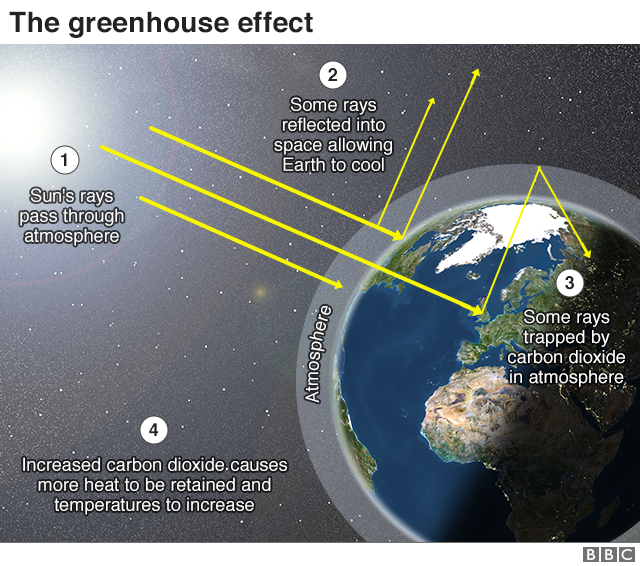



What Is Climate Change A Really Simple Guide c News



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




Greenhouse Gas Effect Stock Image C033 5440 Science Photo Library
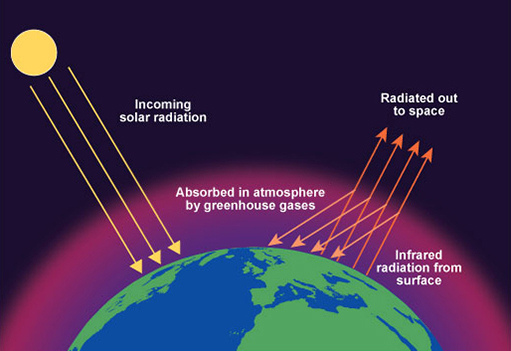



Week 7 The Special Ones 2 2 The Greenhouse Effect Openlearn Open University Exo 1




Greenhouse Effect And Greenhouse Gases Youtube
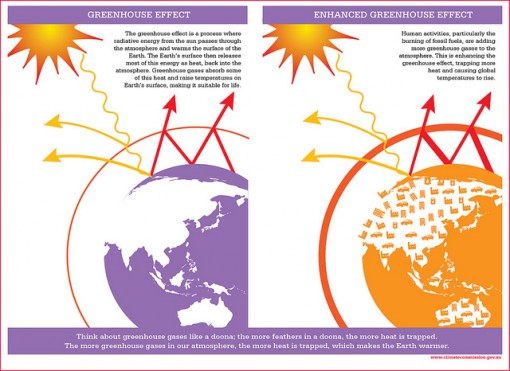



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Conserve Energy Future




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov




Greenhouse Effect Department Of Agriculture Water And The Environment




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica
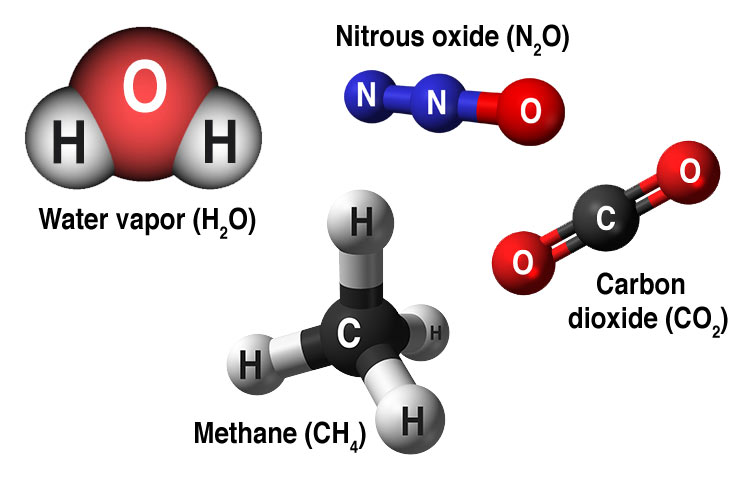



Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet



1




Greenhouse Effect
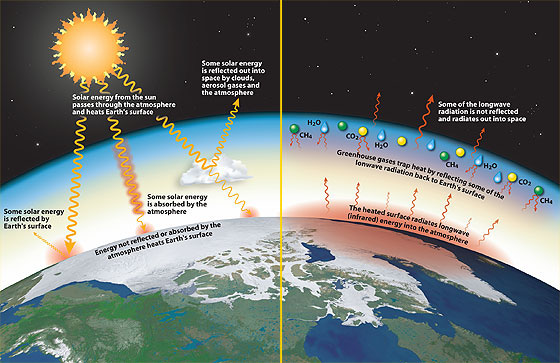



Too Much Of A Good Thing



Greenhouse Gases Impact On Environment Iashe




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc



Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia



Why Are Cfcs More Effective Greenhouse Gas Than Co2 And Ch4 Quora




Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet




The Greenhouse Effect Cool Australia




The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids



3 3 Greenhouse Gases Environmental Change Network




Effects Of Increased Greenhouse Gas Emissions What S Your Impact




Rudn University Scientist Showed Global Warming Effect On Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Paddy Soils Eurekalert Science News



3




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Main Sources Infographic What S Your Impact
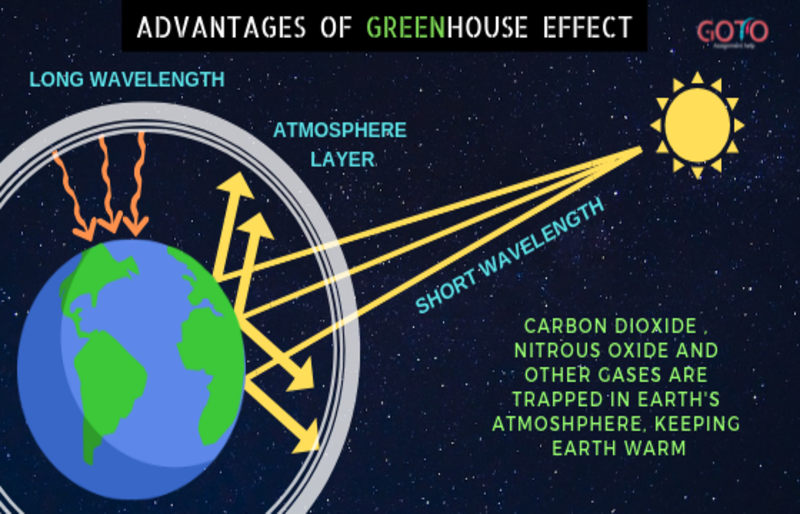



The Advantages Of Greenhouse Effect And The Role Of Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas Global Warming Atmospheric Text Globe Png Pngegg




Air Pollutant Reductions Could Enhance Global Warming Without Greenhouse Gas Cuts




How To Reduce The Emission Of Greenhouse Gas Shouts




Carbon Cycle And Greenhouse Effect A Scientific Infographic




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
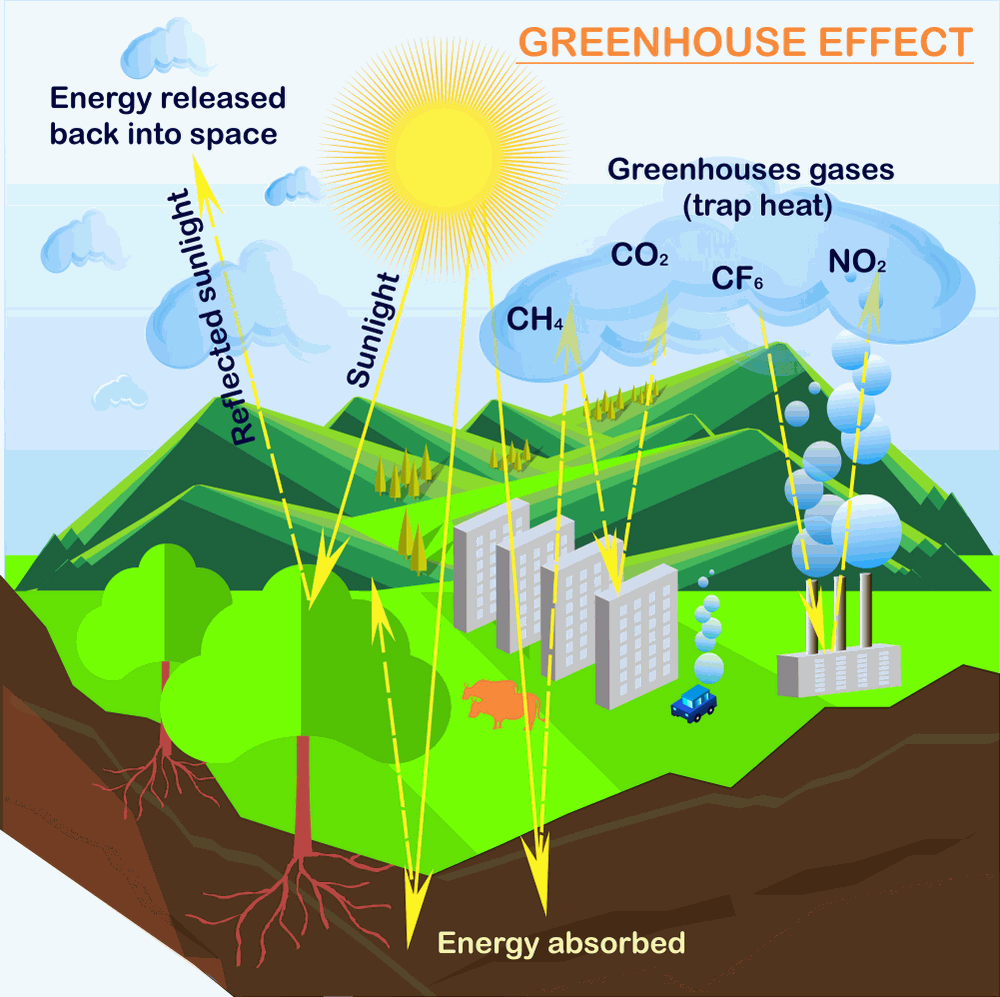



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Global Warming 19
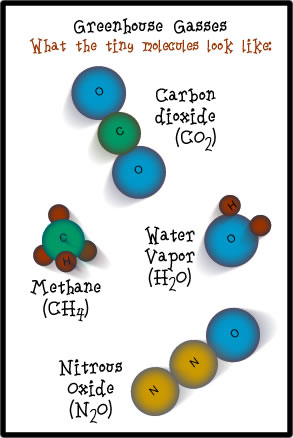



Greenhouse Effect
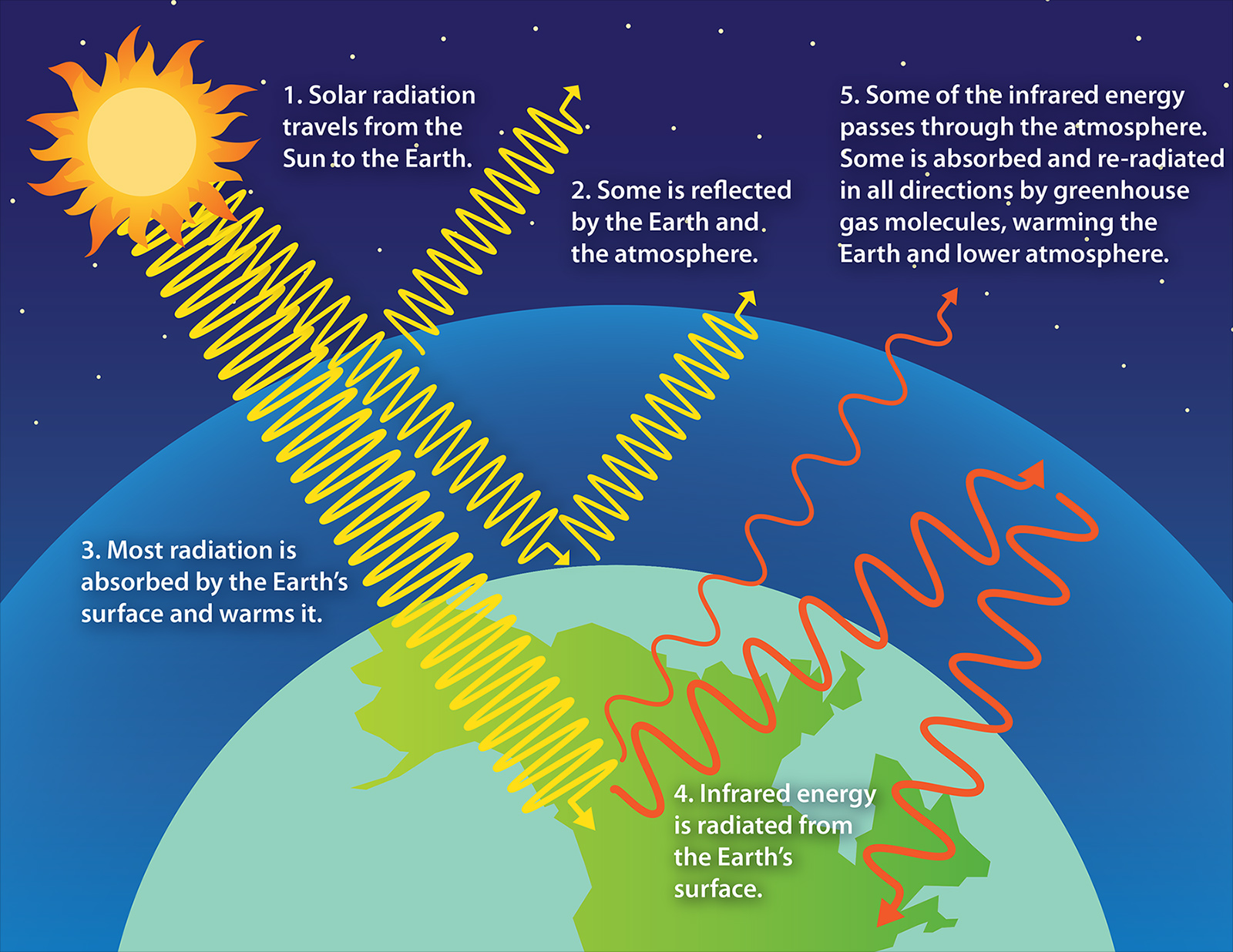



Greenhouse Effect Understanding Global Change




The Greenhouse Effect Ucar Center For Science Education




2c Explore The Greenhouse Effect




What Is Climate Change Climate Assembly
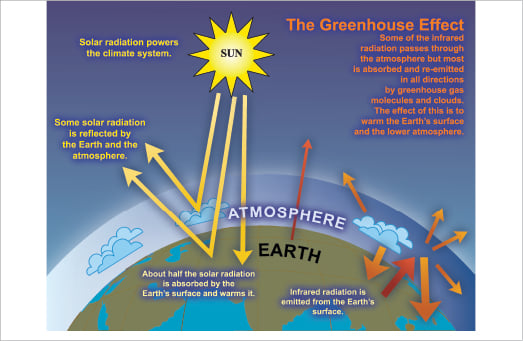



Faq 1 3 Ar4 Wgi Chapter 1 Historical Overview Of Climate Change Science




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Greenhouse Gas Levels In Atmosphere Reach New Record World Meteorological Organization
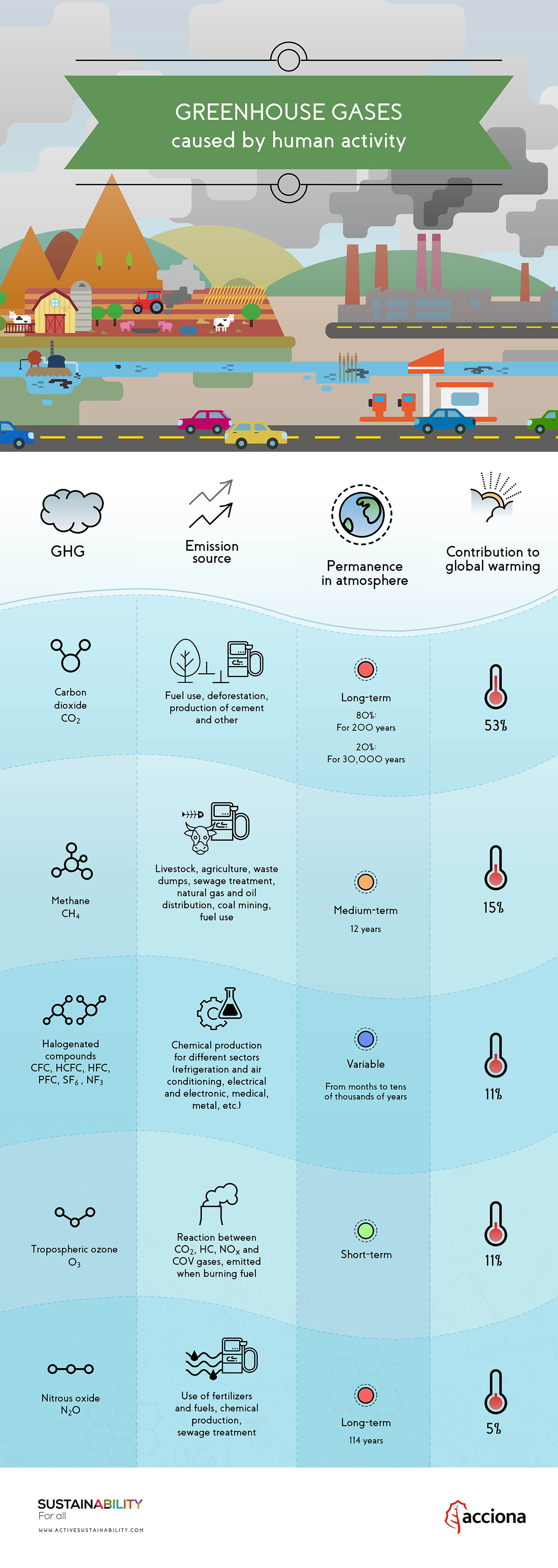



How Do Greenhouse Gases Contribute To Global Warming




Global Warming Green House Effect Ozone Layer Video For Kids Youtube
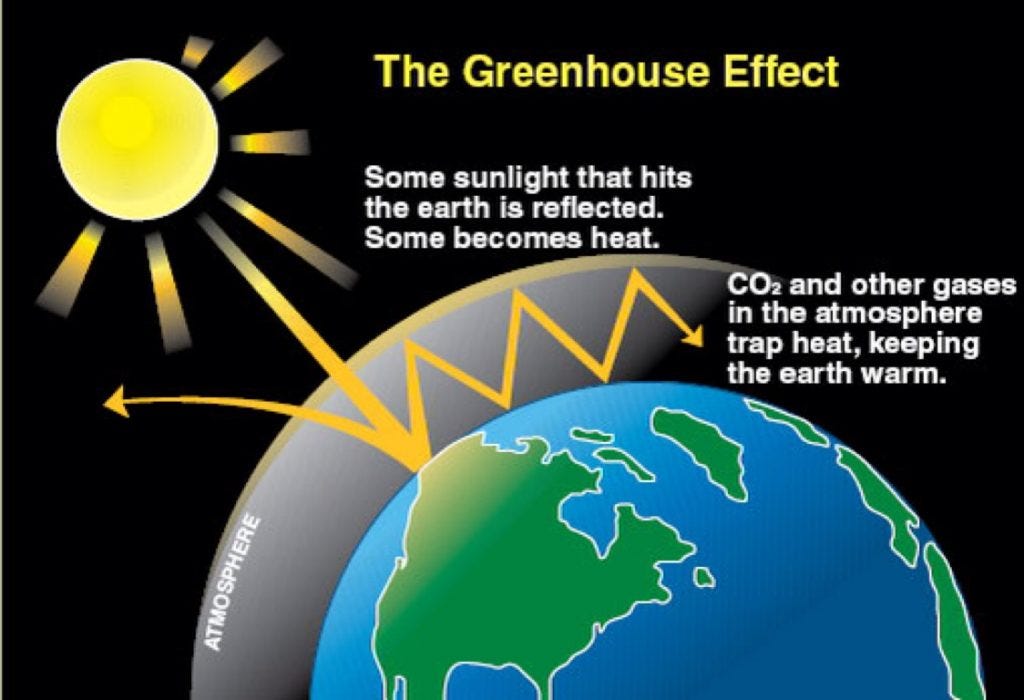



Greenhouse Effect Advantages And Disadvantages By Tutorbin Medium




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa



1




What Are The Greenhouse Gases Infographic 360training




Greenhouse Gases Tips To Reduce Your Greenhouse Gases Delmarfans Com
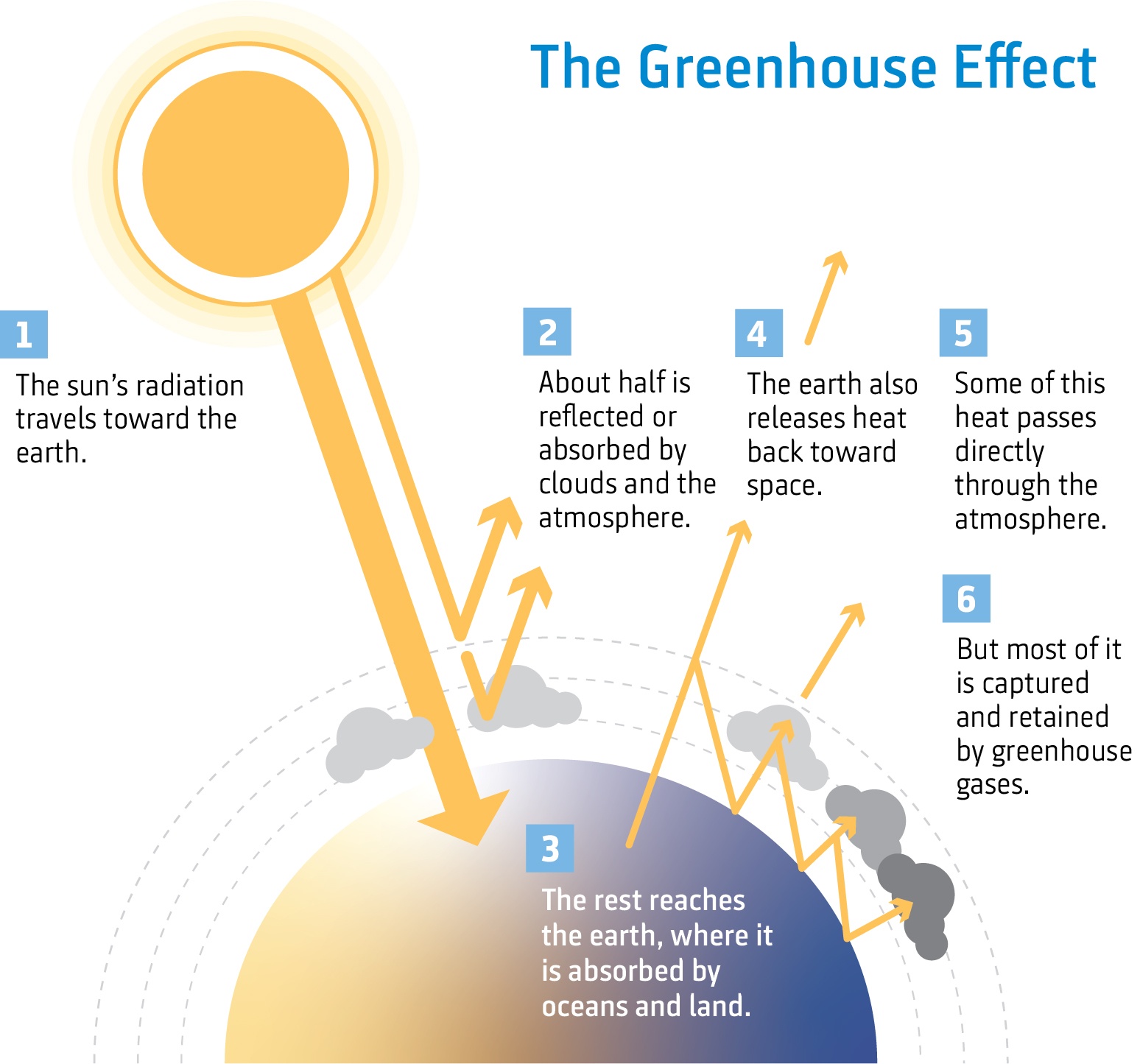



Climate Change The Science Niwa
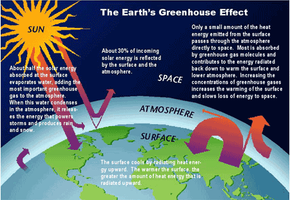



The Greenhouse Effect Howstuffworks




What Is An Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Universe Today




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students




Greenhouse Gases Causes Sources And Environmental Effects Live Science



Q Tbn And9gctoyncs8qyvzsnlf0ehywfdbiqsqkgodl5exlpxd0mjwanu7ugb Usqp Cau



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




Warm On Top Cold Below Unexpected Greenhouse Gas Effect In Lakes
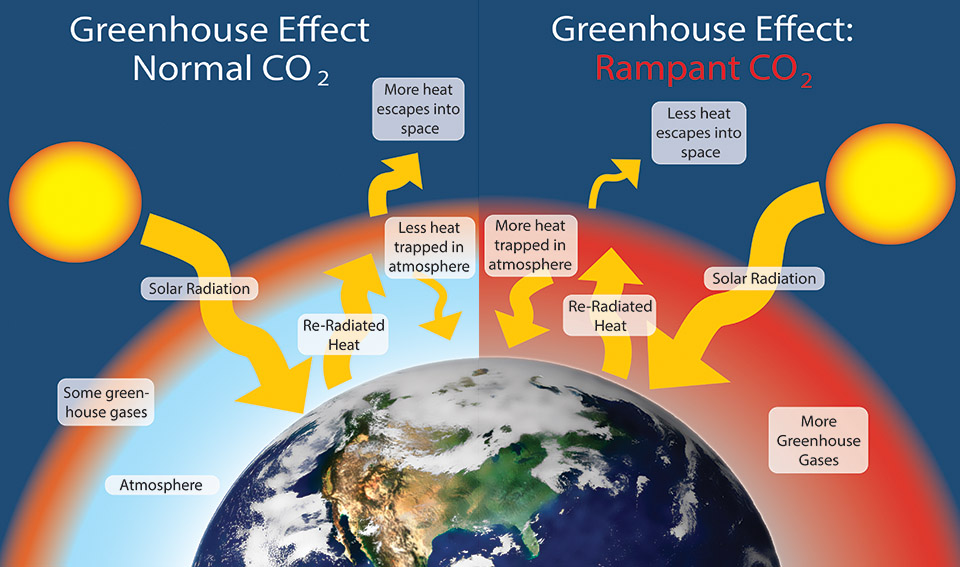



What Is Climate Change Golden Gate National Recreation Area U S National Park Service



Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿